|
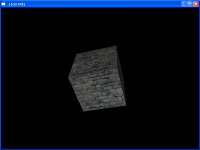
In this tutorial we define a custom material, load a predefined object, and attach the material to it.
We also see a glimpse of how to rotate objects in Rage 3D
This tutorial is a continuation on the previous one called "Creating a Window in Rage 3D"
To define the Custom material we use these functions:
rglAddMaterial
rglAddMaterialTexShader
rglSetMaterialDiffuse
rglSetMaterialAmbient
The rglAddMaterial returns an integer as a refrence to the newly created material so that we can make changes to it later
GCustomMaterialIndex := rglAddMaterial('RockMaterial');
rglAddMaterialTexShader creates a texture shader as a child of the material we just created.
we pass in the GCustomMaterialIndex to tell the engine what material to add the texture shader to.
We also set the texture filtering method of that texture to one of the predefined constants
RGL-TEX-FILTER-TRILINEAR = tri-linear filtering (Best quality)
RGL-TEX-FILTER-BILINEAR = bi-linear filtering (average quality)
RGL-TEX-FILTER-LINEAR = linear filtering (Bad quality)
rglAddMaterialTexShader(GCustomMaterialIndex,'Data\Rock.bmp', RGL-TEX-FILTER-TRILINEAR);
We then set the diffuse and ambient material properties using rglSetMaterialDiffuse and rglSetMaterialAmbient
rglSetMaterialDiffuse(GCustomMaterialIndex,0.6,0.6,0.6);
rglSetMaterialAmbient(GCustomMaterialIndex,0.4,0.4,0.4);
Once we have a material for our cube, we can create a new predefined object of type cube using rglLoadDynamicPredefined
GDynamicCubeIndex := rglLoadDynamicPredefined(RGL-DYN-OBJECT-CUBE,GCustomMaterialIndex,0,0,-20,0,0,0,5,5,5);
Download the code
Please note: In order to use and compile any of these tutotrials, you will need to download the Binary and Art for the engine
|